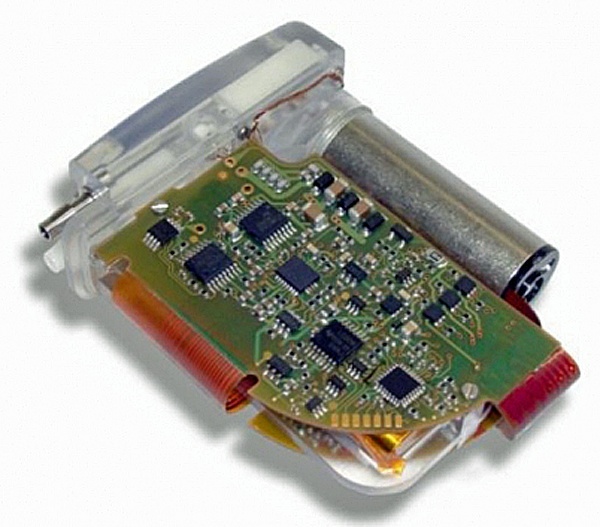
Swiss medical device manufacturer Sequana Medical developed the ALFApump® System to pump fluids accummulated in the abdomen of a patient into the bladder.
Fluid accummulation in the abdomen (ascites) can occur as a symptom of advanced liver disease, certain cancers, or congestive heart failure. When ascites can no longer be managed with medical therapy, redirecting the excess fluid to another body cavity such as the bladder can relieve many of the issues associated with excess fluid accumulation and can reduce the need for repeated invasive intervention.
The ALFApump® System monitors the fluid accumulation in the abdomen and, whenever necessary, pumps the fluid into the bladder of the patient, where it is excreted with the urine. The core component of the three-part system is the ALFApump® implant with the two catheters for the peritoneal cavity and the bladder. The external SmartCharger with charging station is a mobile charging and communication unit that charges the battery of the ALFApump® implant and enables communication. The lithium ion battery of the pump allows autonomous operation for several days. Due to the energy consumption of the pump (per day, 0.9 liter is pumped out on average), the battery has to be charged regularly. The battery is charged wirelessly through the skin of the patient.
The ALFApump® implant is programmable from an external laptop-based programmer that can precisely define how much fluid should be pumped into the bladder per day. The ALFApump® System is CE marked for patients with refractory ascites because of liver disease.