 NeuroTronik, a recent spin-off from Synecor, a Chapel Hill business accelerator, announced that it has raised $13.1M for the development of a neuromodulation system intended for the treatment of acute heart failure syndrome.
NeuroTronik, a recent spin-off from Synecor, a Chapel Hill business accelerator, announced that it has raised $13.1M for the development of a neuromodulation system intended for the treatment of acute heart failure syndrome.
Douglas Reed, a partner in the VC group backing NeuroTronik said that the device aims to shorten hospital stays and reduce the need of patients to return to the hospital a few weeks later. According to Reed:
“It’s a way of stimulating the heart to increase the pumping effectiveness, the effectiveness of the contractions, so it improves cardiac function while the device is in place.”




![logo_mainstay1[1]](https://www.implantable-device.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/logo_mainstay11.jpg)
![SynchroMed-II[1]](https://www.implantable-device.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/SynchroMed-II1-300x272.jpg)
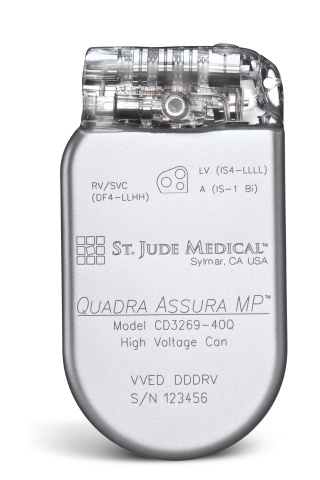 St. Jude Medical today announced CE Mark approval of its next-generation quadripolar device, the Quadra Assura MP™ cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator (CRT-D). The device features MultiPoint™ Pacing (MPP) technology that enables physicians to pace multiple locations on the left side of the heart. This gives the clinician more choices to best optimize cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing to meet individual patient needs.
St. Jude Medical today announced CE Mark approval of its next-generation quadripolar device, the Quadra Assura MP™ cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator (CRT-D). The device features MultiPoint™ Pacing (MPP) technology that enables physicians to pace multiple locations on the left side of the heart. This gives the clinician more choices to best optimize cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing to meet individual patient needs. Sorin announced today CE mark approval and the European commercial launch of the REPLY ™ 200 family of pacemakers featuring Sleep Apnea Monitoring (SAM). According to the press release:
Sorin announced today CE mark approval and the European commercial launch of the REPLY ™ 200 family of pacemakers featuring Sleep Apnea Monitoring (SAM). According to the press release: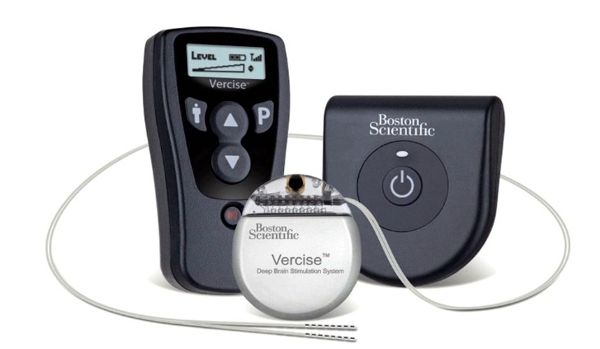

 St. Jude Medical and privately-held Spinal Modulation, Inc., today announced that they have entered into a series of agreements under which St. Jude Medical made a $40 million equity investment in Spinal Modulation, a company that has developed an innovative neuromodulation therapy that provides a new pain management option for patients with chronic, intractable pain.
St. Jude Medical and privately-held Spinal Modulation, Inc., today announced that they have entered into a series of agreements under which St. Jude Medical made a $40 million equity investment in Spinal Modulation, a company that has developed an innovative neuromodulation therapy that provides a new pain management option for patients with chronic, intractable pain.