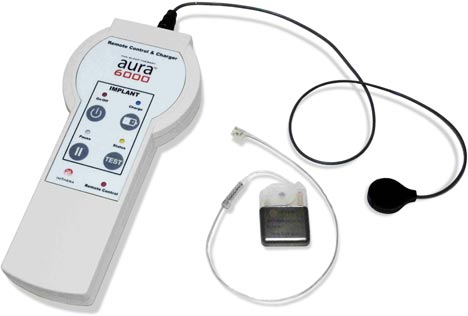
Image Credit: Imthera
ImThera Medical announced this week that it received the CE Mark for the Aura6000 System to Treat Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Continue reading

Image Credit: Imthera
ImThera Medical announced this week that it received the CE Mark for the Aura6000 System to Treat Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Continue reading→

Image Credit: Boston Scientific
Boston Scientific announced the exercise of its option to acquire Cameron Health. Cameron Health developed the world’s first and only commercially-available subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator – the S-ICD® System that I blogged about a few weeks ago.
The agreement calls for an upfront payment of $150 million, payable upon transaction closing, an additional potential $150 million payment upon FDA approval of the S-ICD System, plus up to an additional $1.050 billion of potential payments upon achievement of specified revenue-based milestones over a six-year period following FDA approval. Closing of the transaction is subject to customary conditions, including relevant antitrust clearance, and is expected to occur in the second or third quarter of 2012.
Image Credit: Medtronic
Medtronic today announced the receipt of CE Mark and launch of the CapSure Sense MRI™ SureScan® pacing leads, which are approved for use during MRI procedures. The newly approved leads are the smallest MR–Conditional leads available in the world with a 5.3 French isodiametric lead body. The new leads are passive-fixation leads. Previously approved Medtronic MR–Conditional leads are active fixation leads.
Click here for Medtronic’s product page for the CapSure Sense MRI™ SureScan® Pacing Leads.

Image Credit: Stanford University
Stanford Engineering assistant professor Ada Poon demonstrated a tiny, wirelessly powered, self-propelled medical device capable of controlled motion through blood. The device drives electrical current directly through the fluid, which in the presence of an external magnetic field creates a directional force that pushes the device forward. This type of device is capable of moving at just over half-a-centimeter per second.
That was the news picked up by bloggers from Poon’s presentation at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC). However, what caught my attention is her work on inductive transcutaneous energy transmission. From Stanford’s press release: Continue reading→

Today Medtronic announced financial results for its third quarter of fiscal year 2012, which ended January 27, 2012. According to the report:
“CRDM third quarter revenue of $1.192 billion decreased 2 percent as reported or 3% on a constant currency basis. Third quarter revenue from ICDs was $674 million, down 9 percent on a constant currency basis, while pacing revenue was $467 million, an increase of 3 percent on a constant currency basis. Weaker ICD sales, primarily due to declining procedure volumes in the U.S. market versus the prior year, were partially offset by continued growth of the AF Solutions and Pacing businesses.”
…
“Neuromodulation revenue of $419 million increased 4 percent as reported and on a constant currency basis. Growth continues to be driven by strong sales of InterStim® Therapy. The RestoreSensor™ spinal cord stimulator with its proprietary AdaptiveStim™ technology continues to perform well in Europe, and was approved in the U.S. and Japan in the third quarter. The U.S. launch of this product was delayed for most of the quarter due to a supply disruption resulting from the flooding in Thailand, which has subsequently been resolved.”

Image Credit: MicroCHIPS, Inc.
Last month I posted some background on MicroCHIPS, the MIT spinoff to develop implantable sensors and drug-delivery devices. I concluded that post with the February 2011 announcement that MicroCHIPS started its clinical trial to assess the pharmacokinetics of long-term parathyroid hormone (hPTH 1-34) delivery in women with osteoporosis.
MicroCHIPS announced today the results of the first successful human clinical trial with an implantable, wirelessly controlled and programmable microchip-based drug delivery device. The MicroCHIPS study was published in today’s online edition of the journal Science Translational Medicine. Continue reading→
My friend and colleague Dr. Irit Yaniv alerted me to this iPhone app that was just released. It is an implantable pacemaker and defibrillator database that, according to its author, displays up to 70 parameters for each model, includes battery and longevity data, and links directly to product manuals. Continue reading→
 In 1965, Australian medical device pioneer Noel Gray established Telectronics – Australia’s first manufacturing facility for producing pacemakers that were designed in-house. Telectronics was an innovative developer, achieving some major successes in the early cardiac pacing field, for example, Telectronics’ leads allowed narrowing the pacing pulse to its current nominal of 0.5 milliseconds; encapsulating the pacemaker in titanium instead of epoxy; using a microplasma weld to join the two halves of the pacemaker capsule; creating one of the first rate-responsive ‘demand’ pacemakers; and isolating the pacemaker’s battery in a separate compartment to deal with the problem of leaking mercury-zinc batteries. Continue reading→
In 1965, Australian medical device pioneer Noel Gray established Telectronics – Australia’s first manufacturing facility for producing pacemakers that were designed in-house. Telectronics was an innovative developer, achieving some major successes in the early cardiac pacing field, for example, Telectronics’ leads allowed narrowing the pacing pulse to its current nominal of 0.5 milliseconds; encapsulating the pacemaker in titanium instead of epoxy; using a microplasma weld to join the two halves of the pacemaker capsule; creating one of the first rate-responsive ‘demand’ pacemakers; and isolating the pacemaker’s battery in a separate compartment to deal with the problem of leaking mercury-zinc batteries. Continue reading→

Image Credit: Micro Systems Technologies
Micro Systems Technologies (MST) is the vertically-integrated supplier of microelectronics and implantable-grade components to Biotronik. It now offers its development and manufacturing services to others.
Through its companies, MST offers high-reliability microelectronic modules for implantable medical devices such as pacemakers, defibrillators, neurostimulators, and cochlear implants.
MST can provide integrated solutions encompassing everything from conceptual design through high-volume surface-mount (SMT) assembly of modules. Services include design development of customer-defined electronic modules, custom ASIC design and development, and high-density-interconnect (HDI) substrate and assembly design.
As a OEM, MST offers state-of-the-art automated SMT line, an ISO 13485–compliant process and component verification and validation methodology, a manufacturing execution system that automates data collection, analysis, and process control, and comprehensive supply-chain management and monitoring with 100% traceability. Continue reading→

Image Credit: VeriMed
On January 17, 2012, VeriTeQ Acquisition Corporation of Delray Beach, FL announced that it acquired the VeriChip implantable RFID technology and its related Health Link personal health record from PositiveID Corporation. Continue reading→

Image Credit: St. Jude Medical
Today Boston Scientific Corporation announced financial results for the fourth quarter and full year ended December 31, 2011. Summarizing the AIMD data:
Click here for the news release.
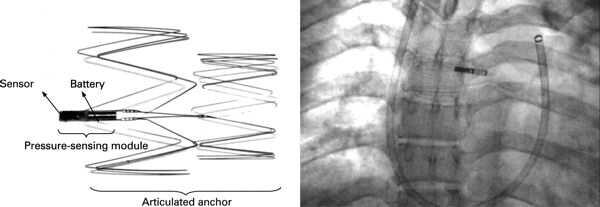
Remon Medical Technologies, Ltd. was founded in 1997 in Caesarea, Israel to develop implantable, wireless pressure sensors.
Remon developed an implantable hemodynamic monitor, which allowed on-demand, non-invasive, leadless self-monitoring of pulmonary artery pressure by the patient at home. ImPressure devices were placed in the pulmonary artery, and transmitted pressure readings to a hand-held monitor. It was hoped that the system would provide early warning of the need for treatment, avoiding hospitalization and deterioration in the patient’s condition. Continue reading→

Image Credit: Purdue University
A group of researchers at Purdue University led by Prof. Babak Ziaie developed a vibrating cantilever that is excited by an external bass source from 200-500 Hz. The excitation causes the cantilever to vibrate, generating electricity and storing a charge in a capacitor.
Although playing tones within a certain frequency range would be ideal, the group concentrated on the use of music as an excitation source. According to the researchers, “a plain tone is a very annoying sound. We thought it would be novel and also more aesthetically pleasing to use music.” Continue reading→
 Sensors for Medicine and Science, Inc. (SMSI) of Germantown, MD was founded in 1997 to develop chemical sensing technologies based on fluorescence sensing.
Sensors for Medicine and Science, Inc. (SMSI) of Germantown, MD was founded in 1997 to develop chemical sensing technologies based on fluorescence sensing.
SMSI® is now developing an implantable glucose sensor that is designed to automatically measure interstitial glucose every few minutes. The sensor implant communicates wirelessly with a small external reader, allowing it to track the rate of change of glucose levels and warn the user of impending hypo- or hyperglycemia. According to SMSI, the target operational life of the sensor implant will be 6-12 months, after which it would be replaced. Continue reading→